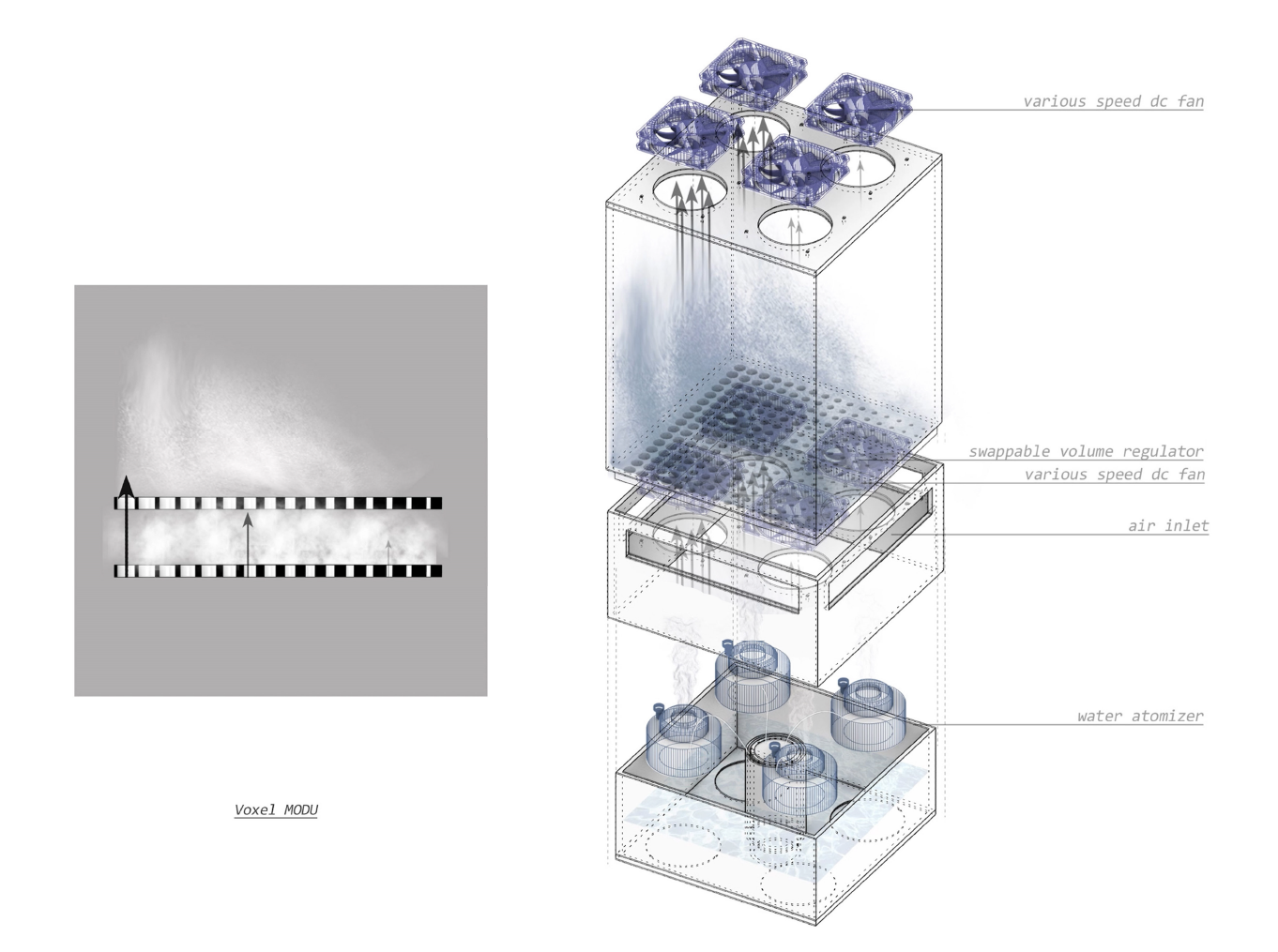
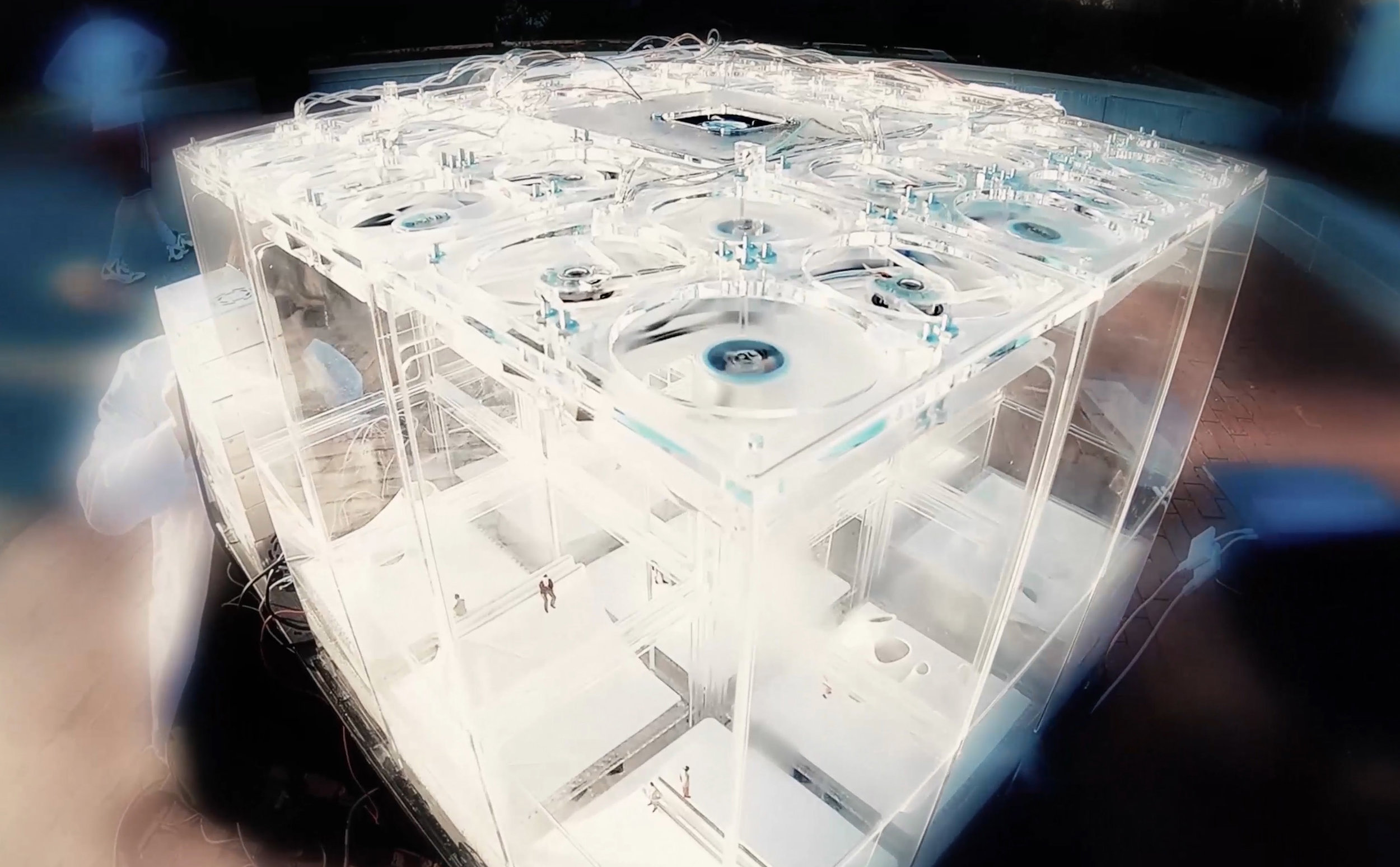
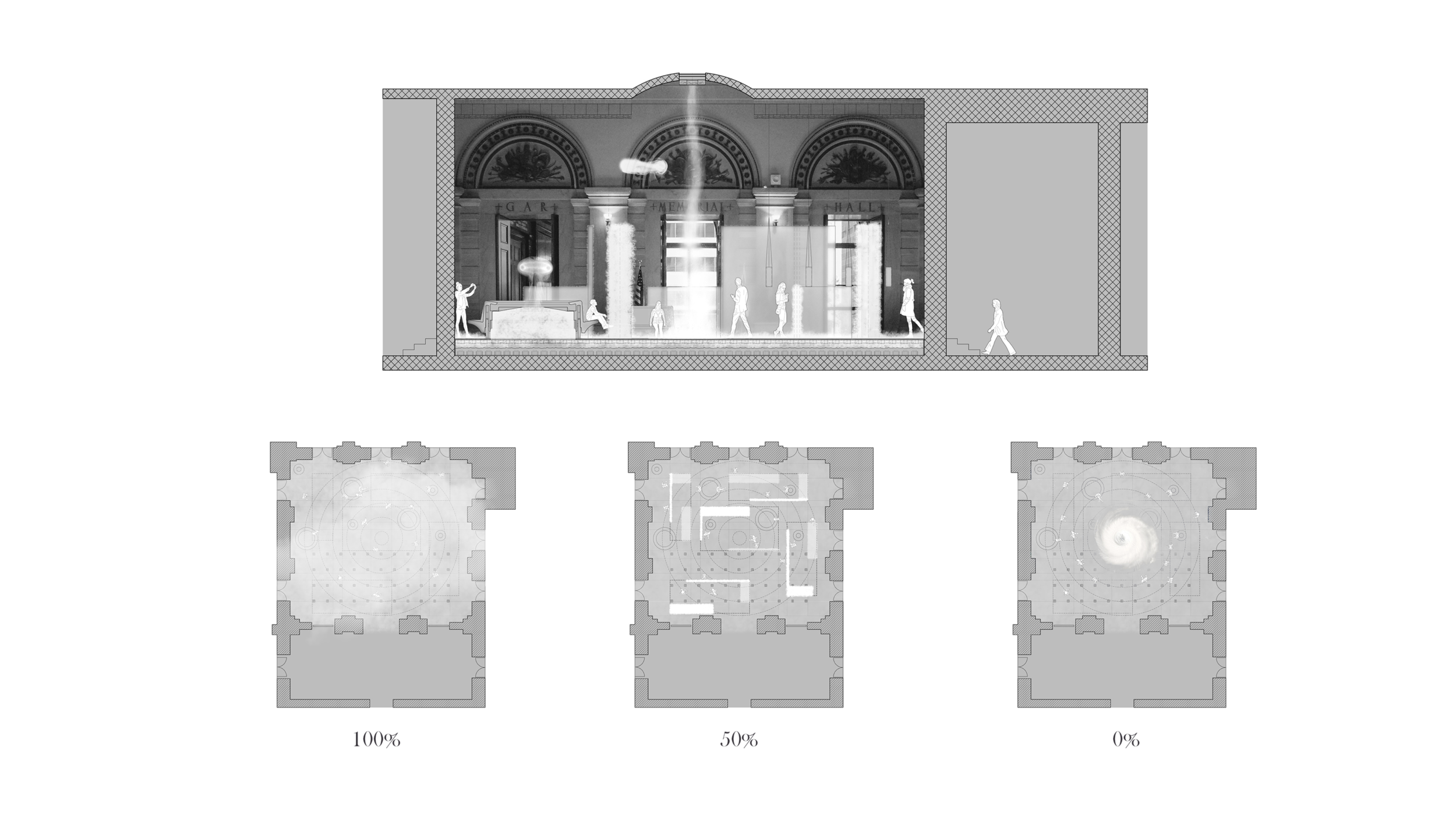
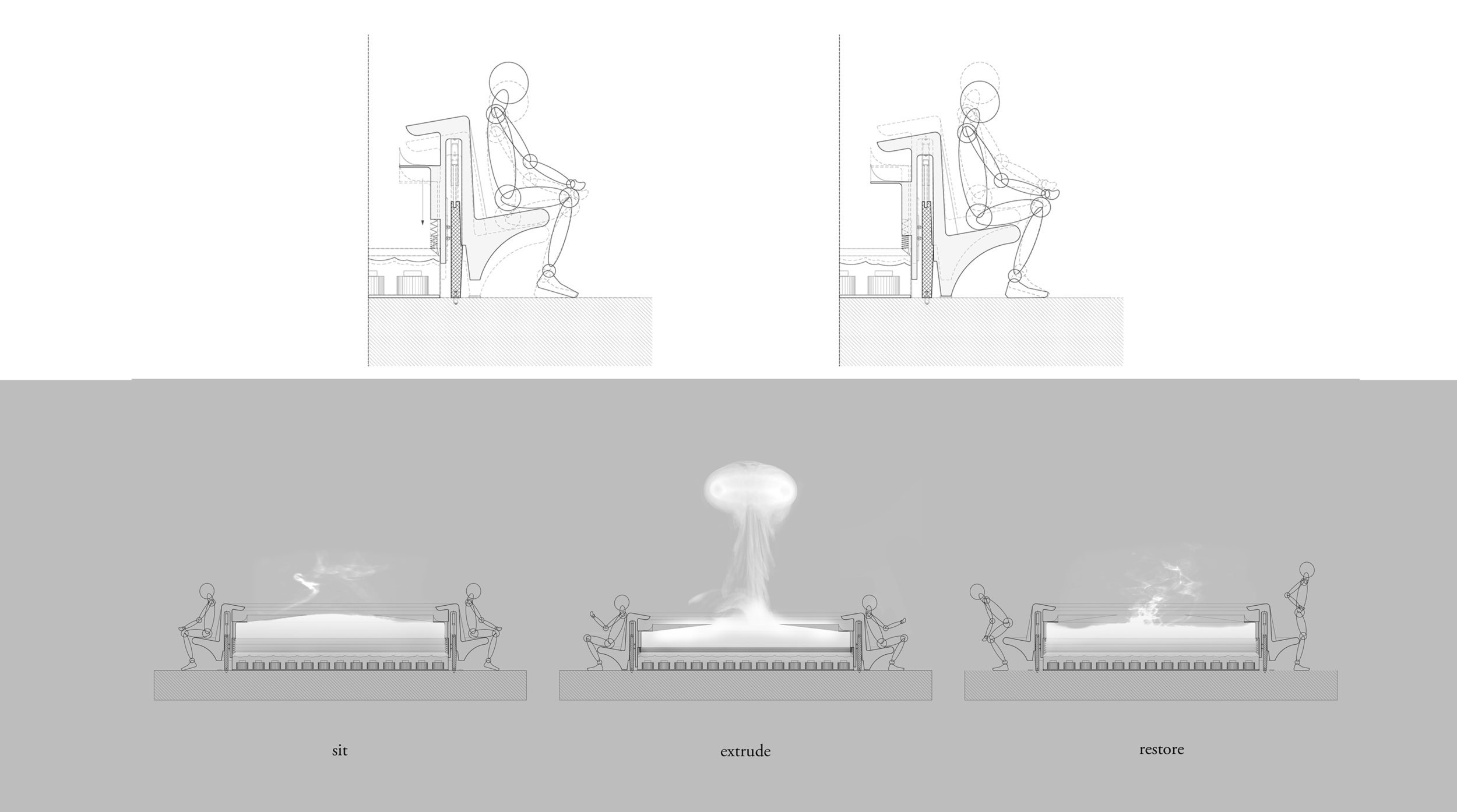
Diffusive Geometry:
Vapor as a Tectonic Element to Sculpt Microclimates in Architectural Space
Architecture primarily serves as a way to create and control the environment around us. Unlike natural weather, climate conditions in architecture are often static and binary, with no diffusion in between. As a result, sensory experiences that are directly accessible outdoors, like atmospheric quality, diffusiveness, and flow, are completely excluded from the indoors. The climate is discretized in space into strict self-contained, functional units, where wetness is kept in wet spaces yet other areas are completely dry.
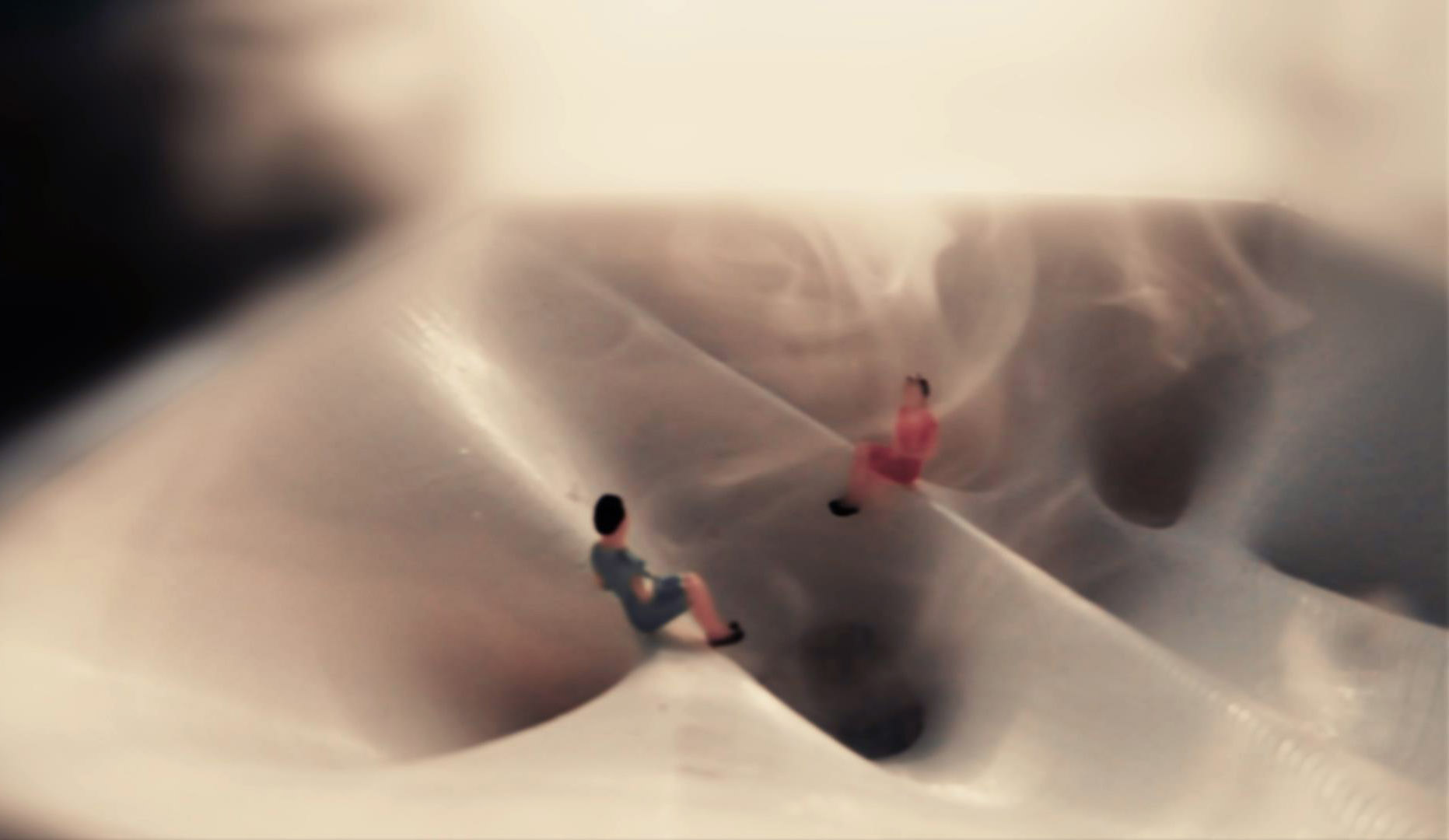
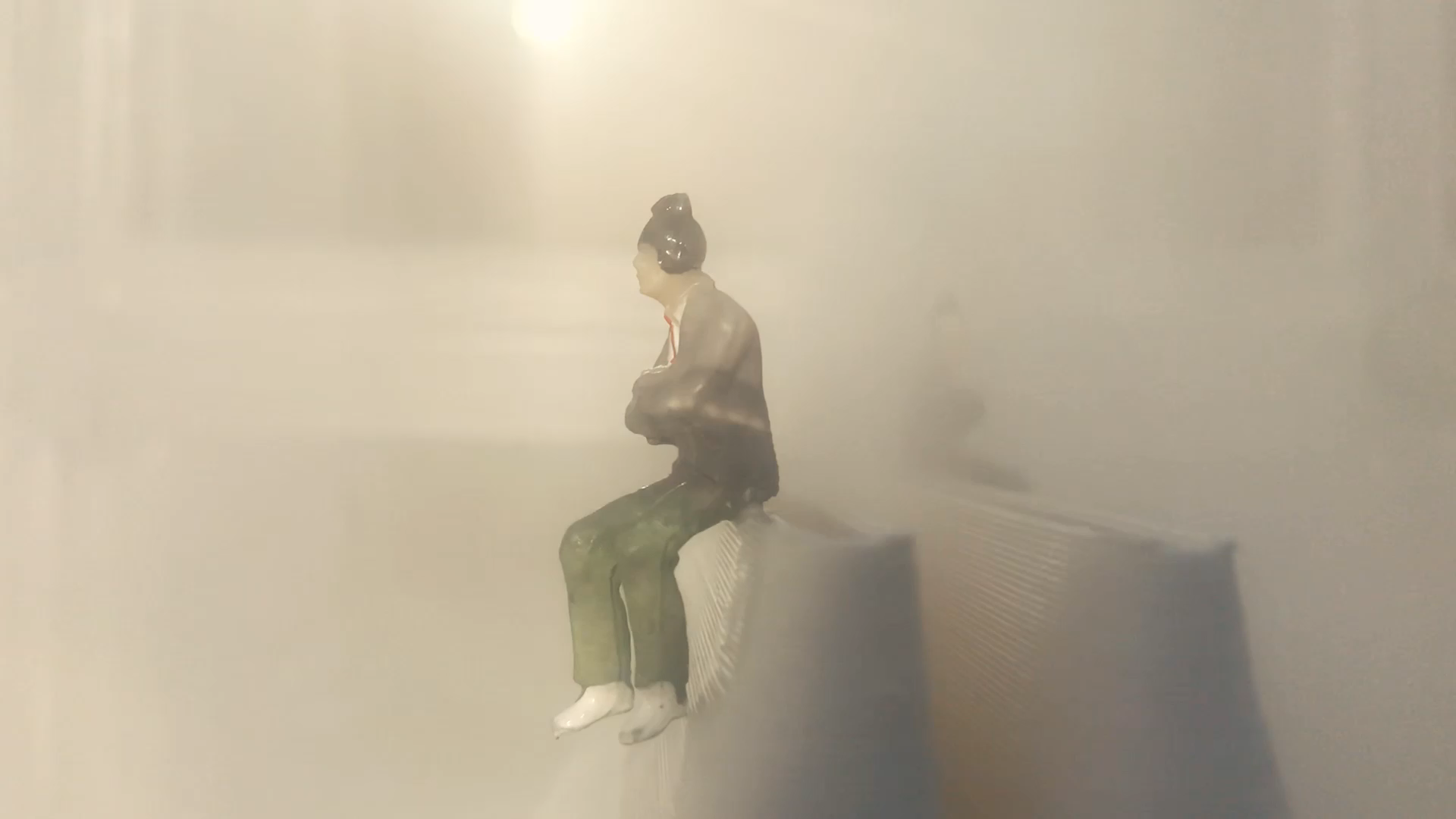
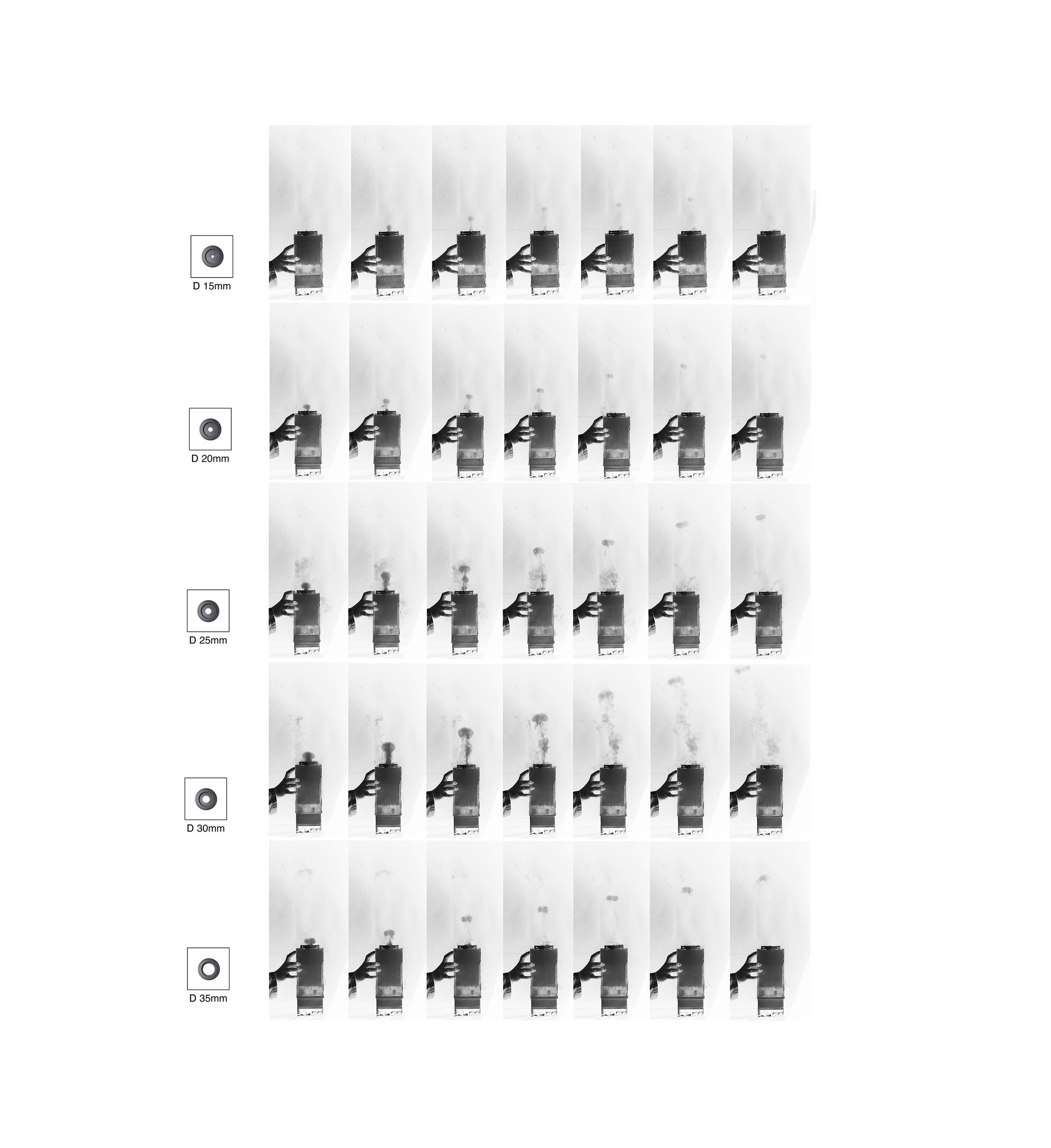
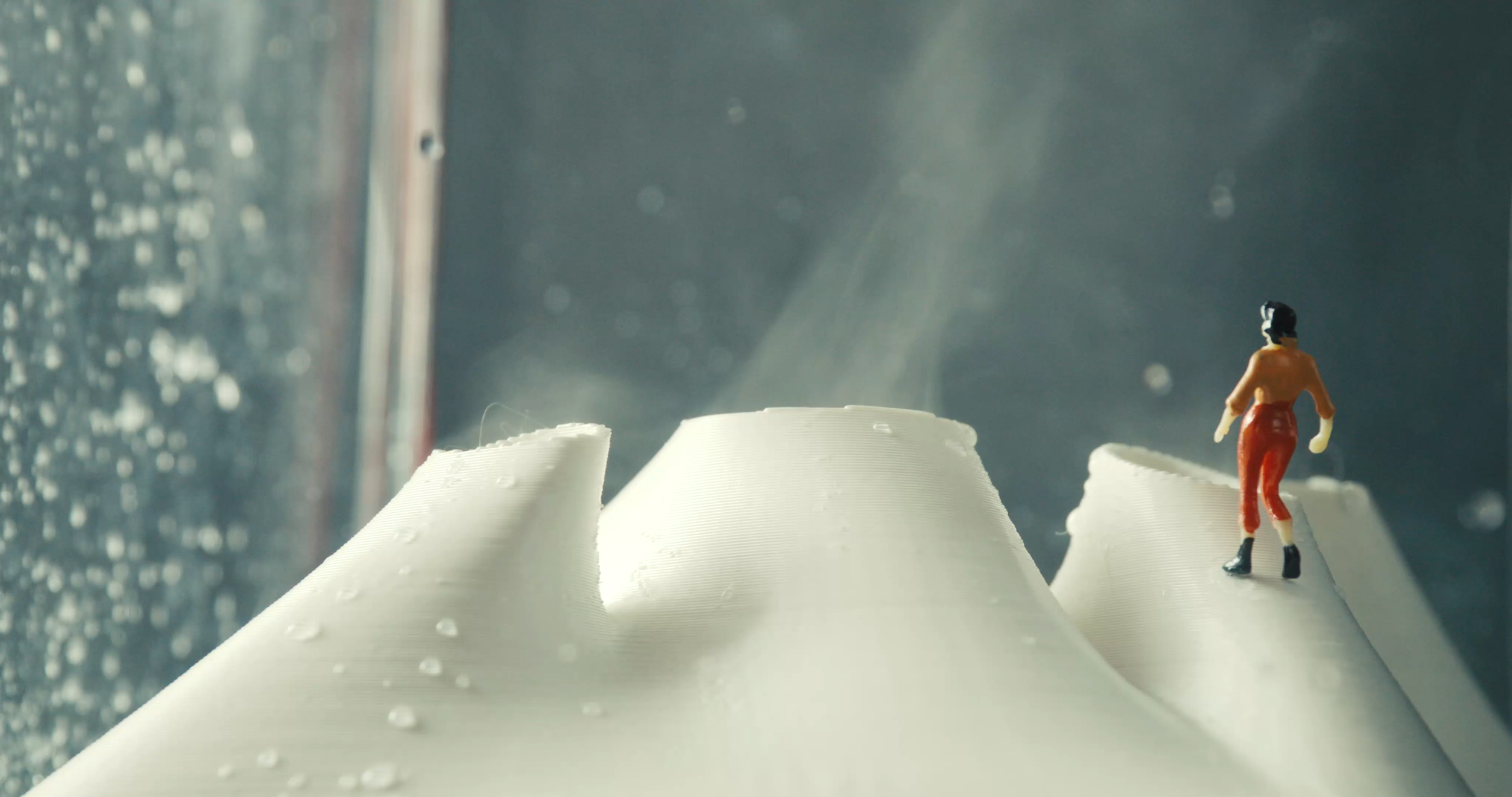
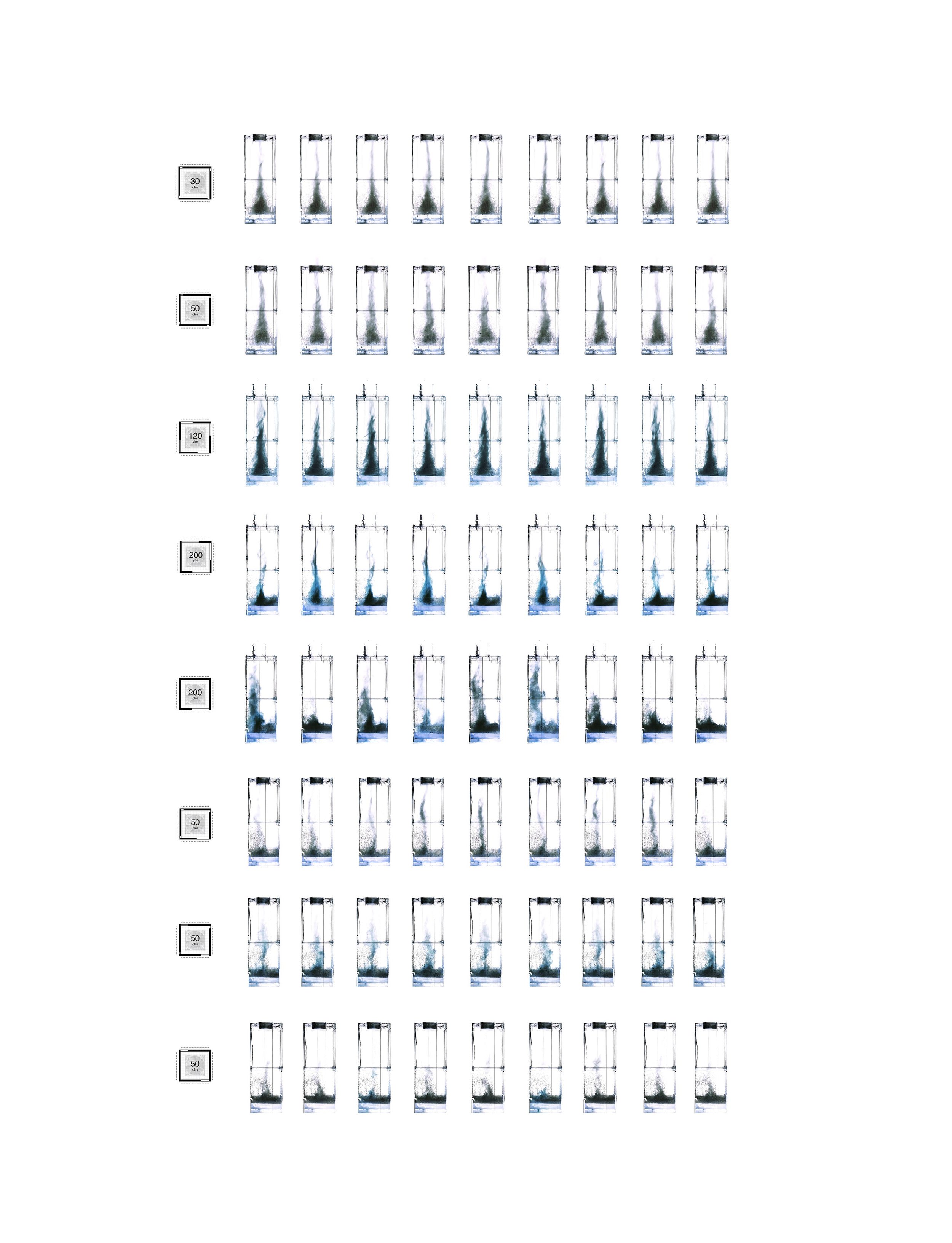
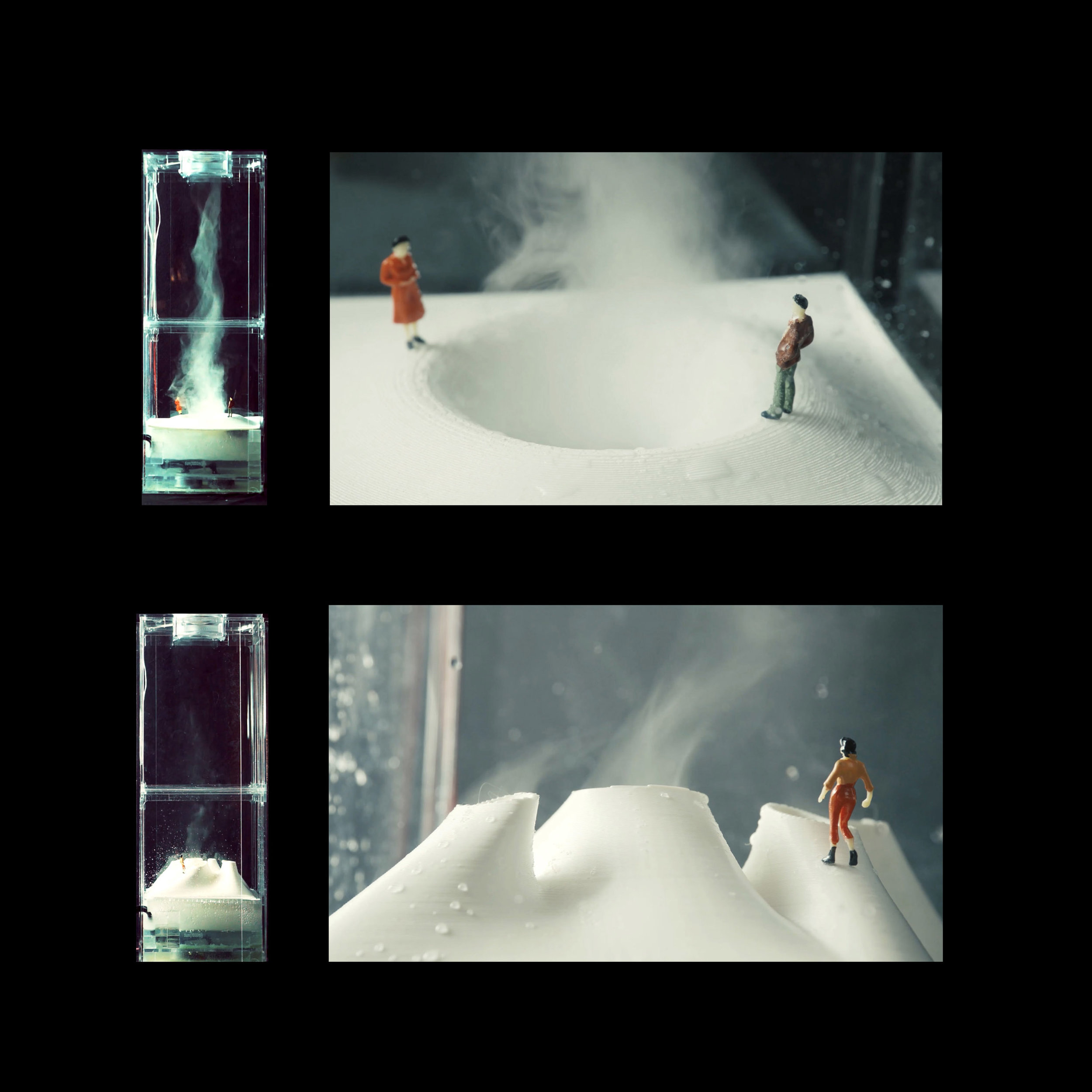
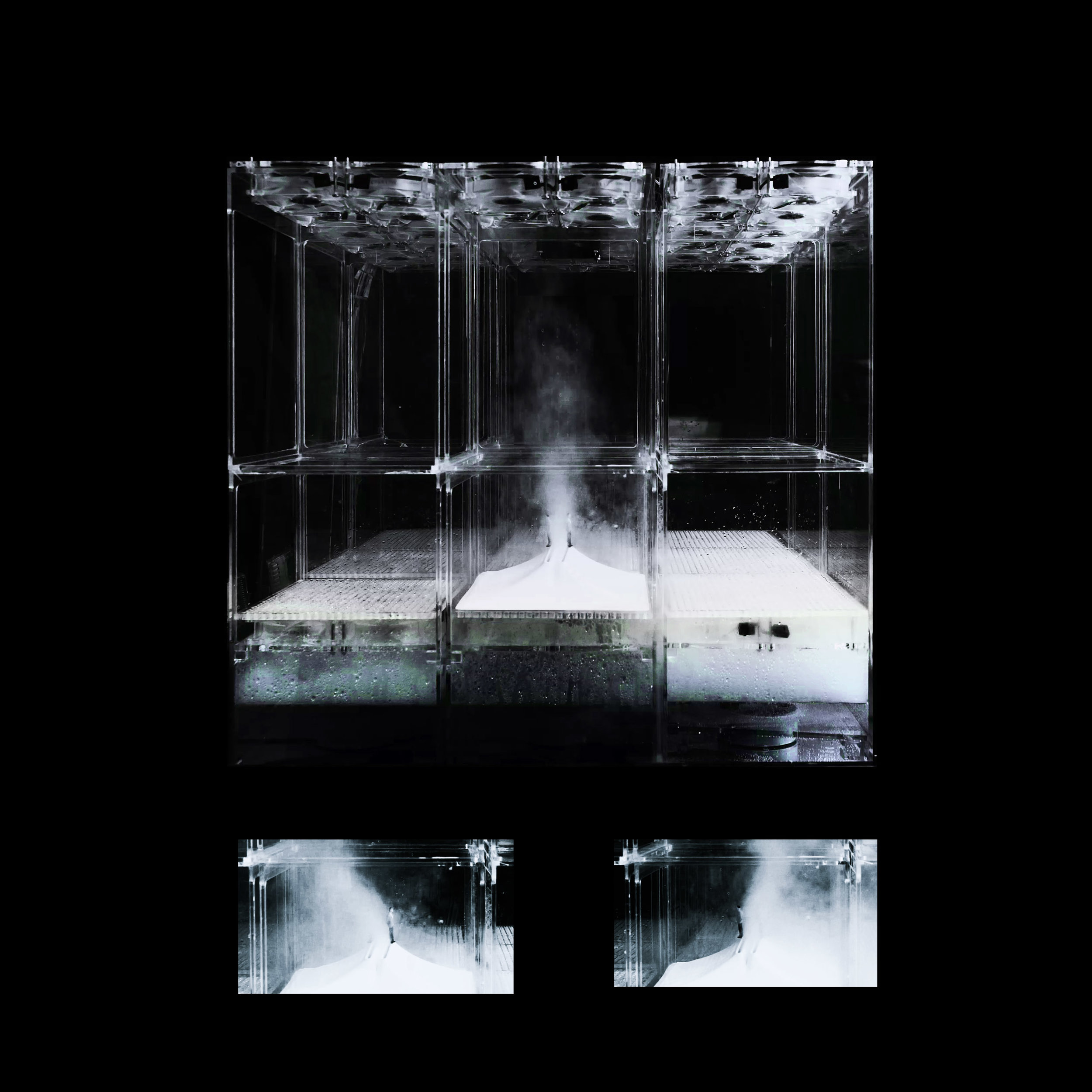
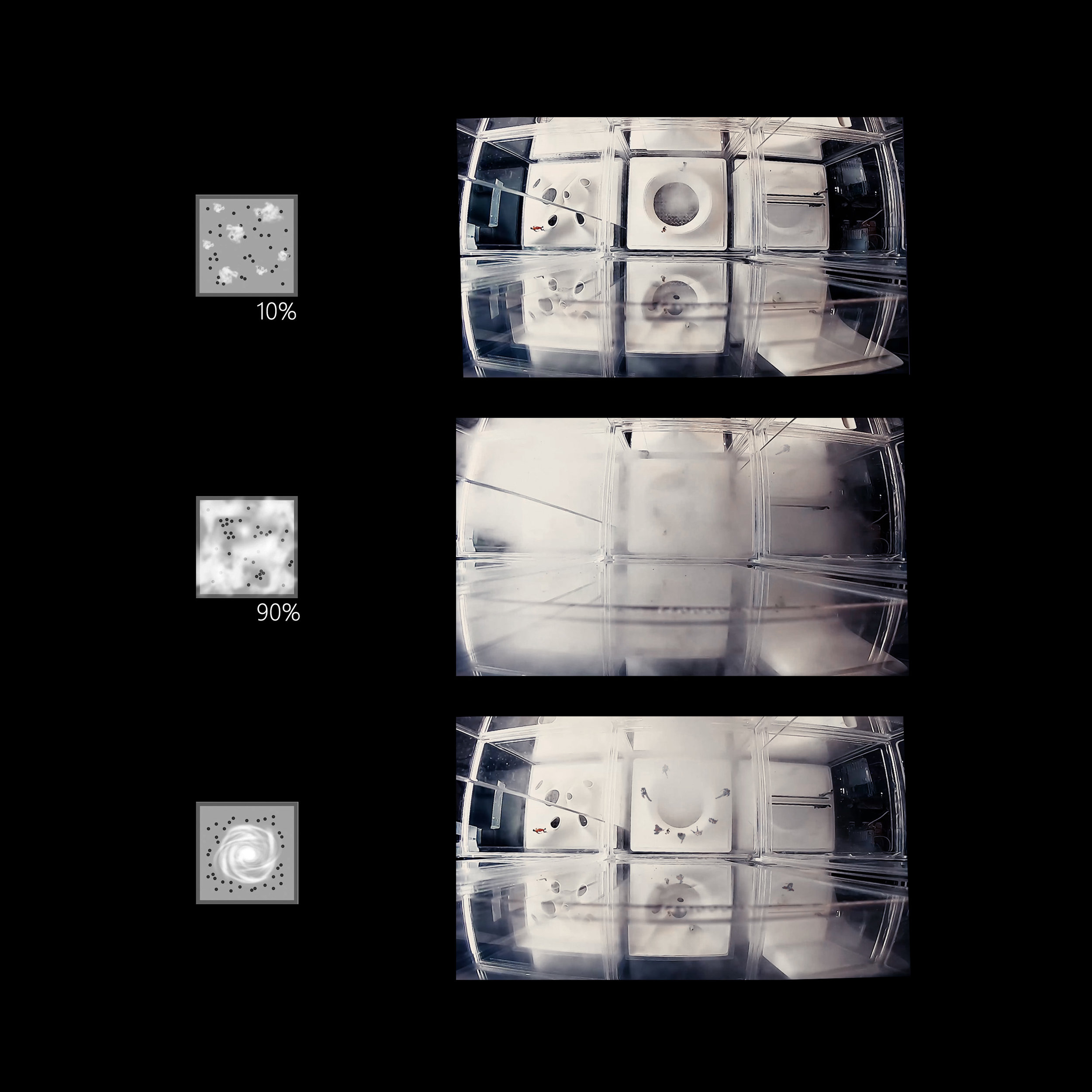
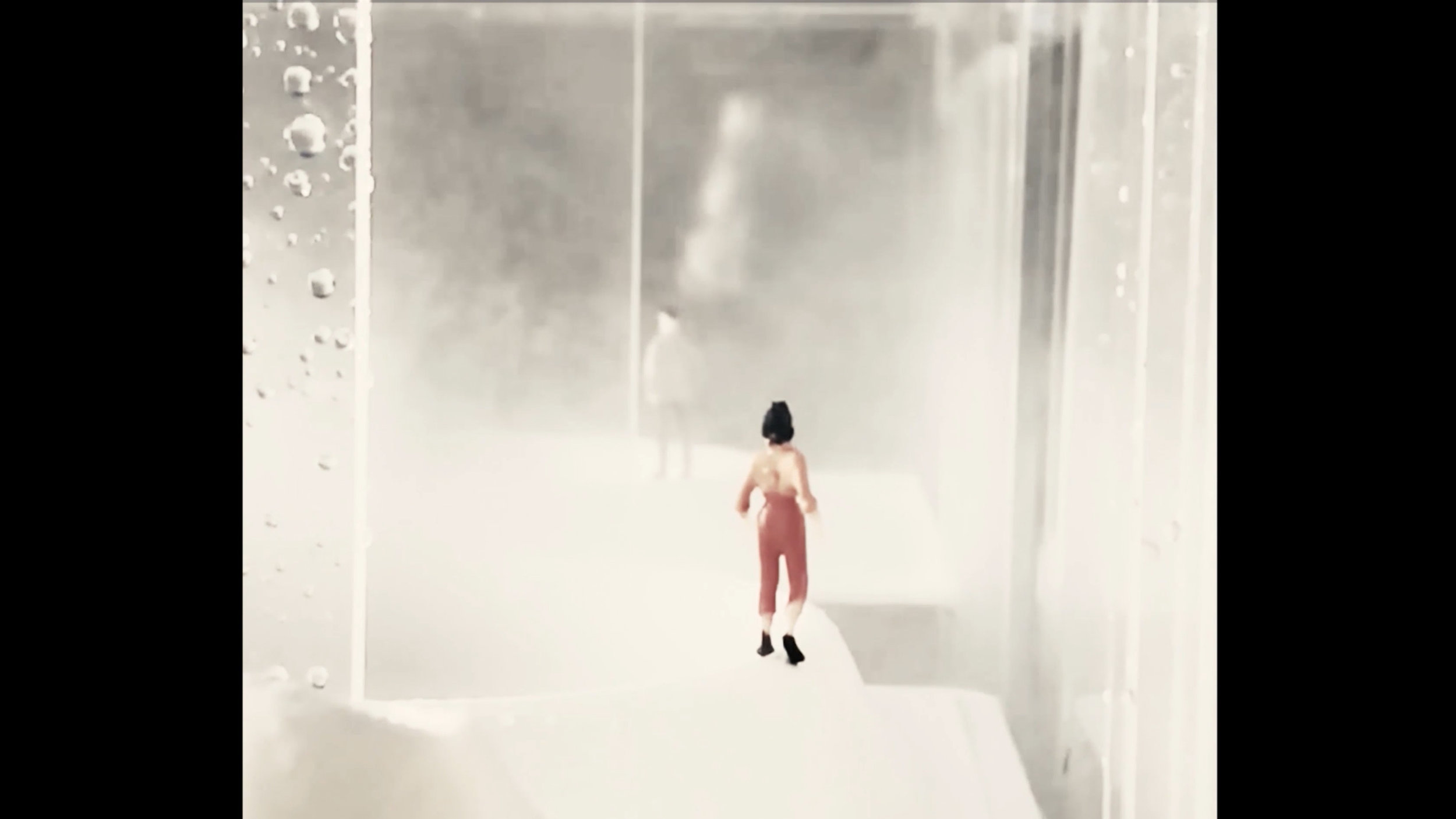
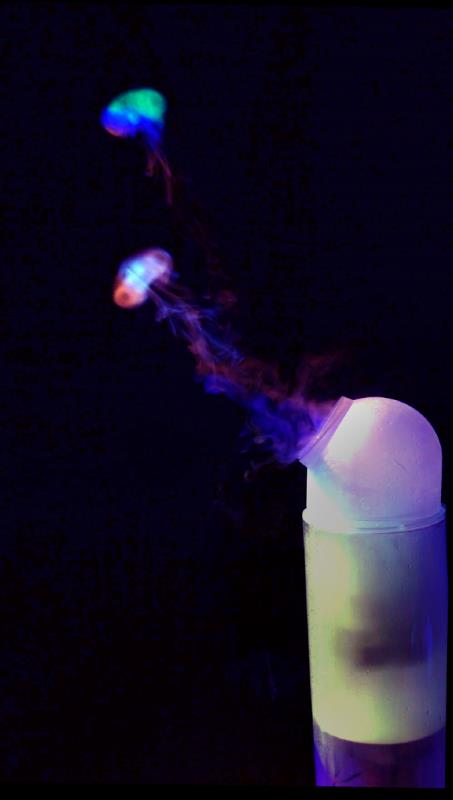
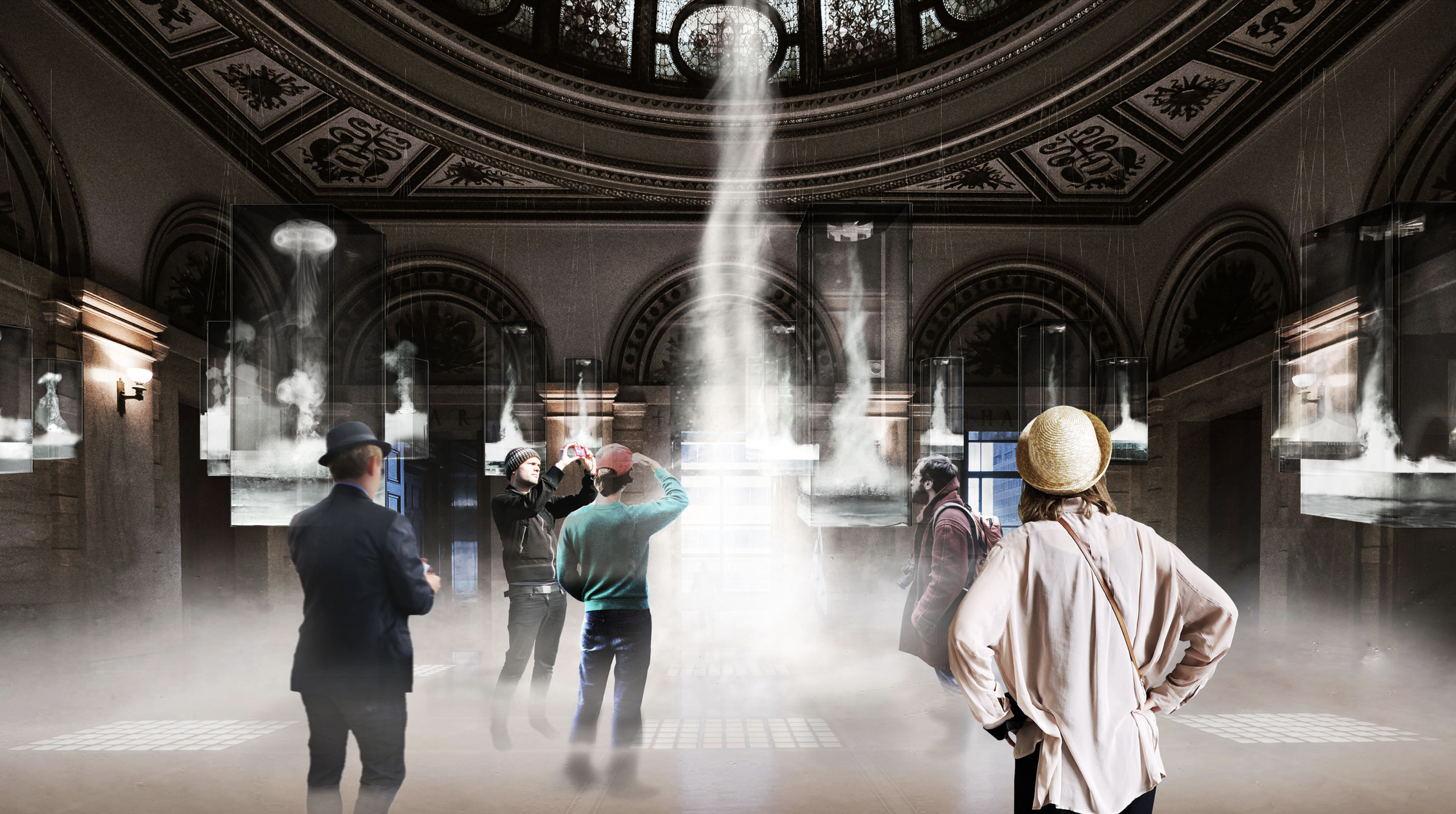
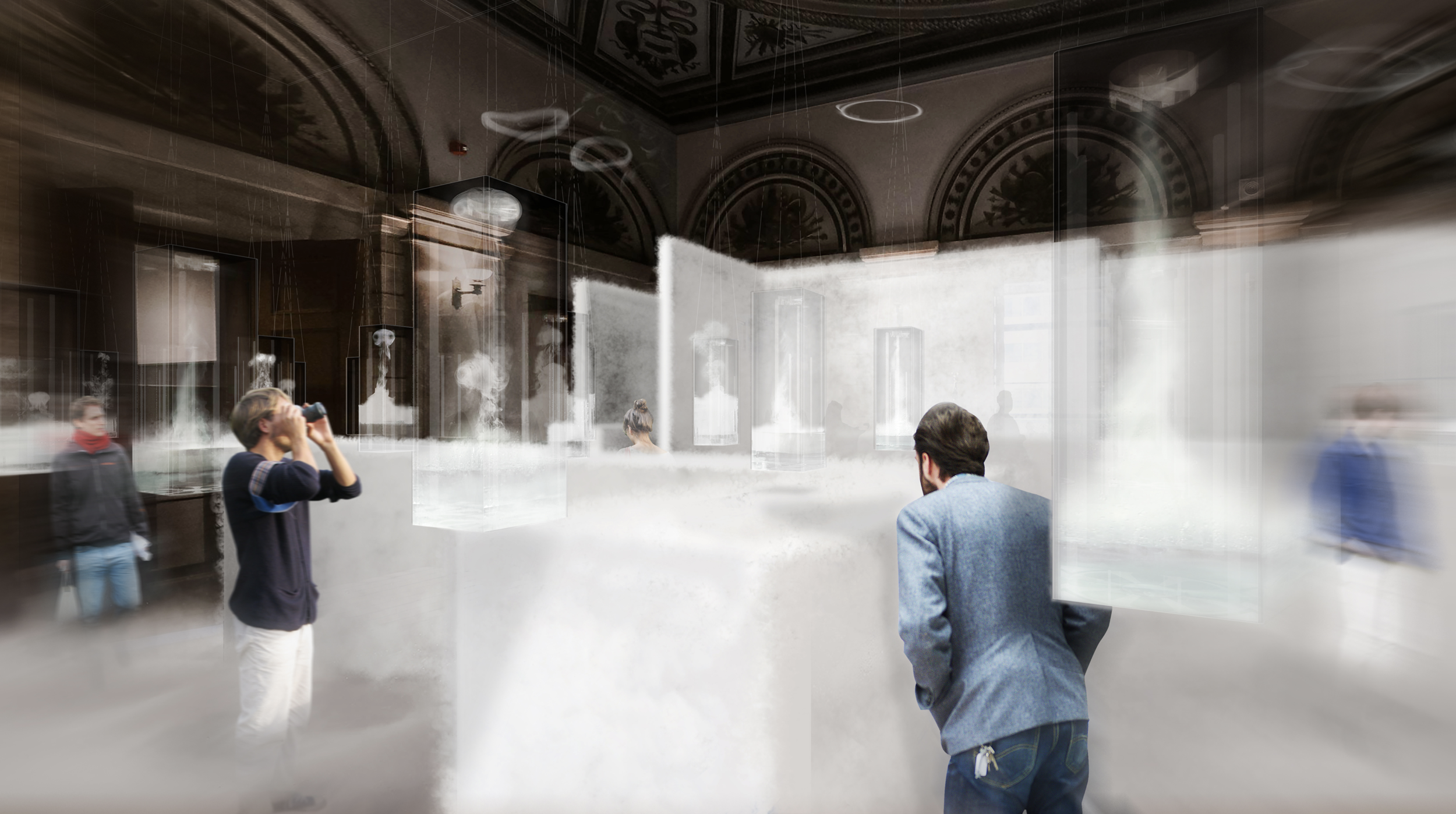
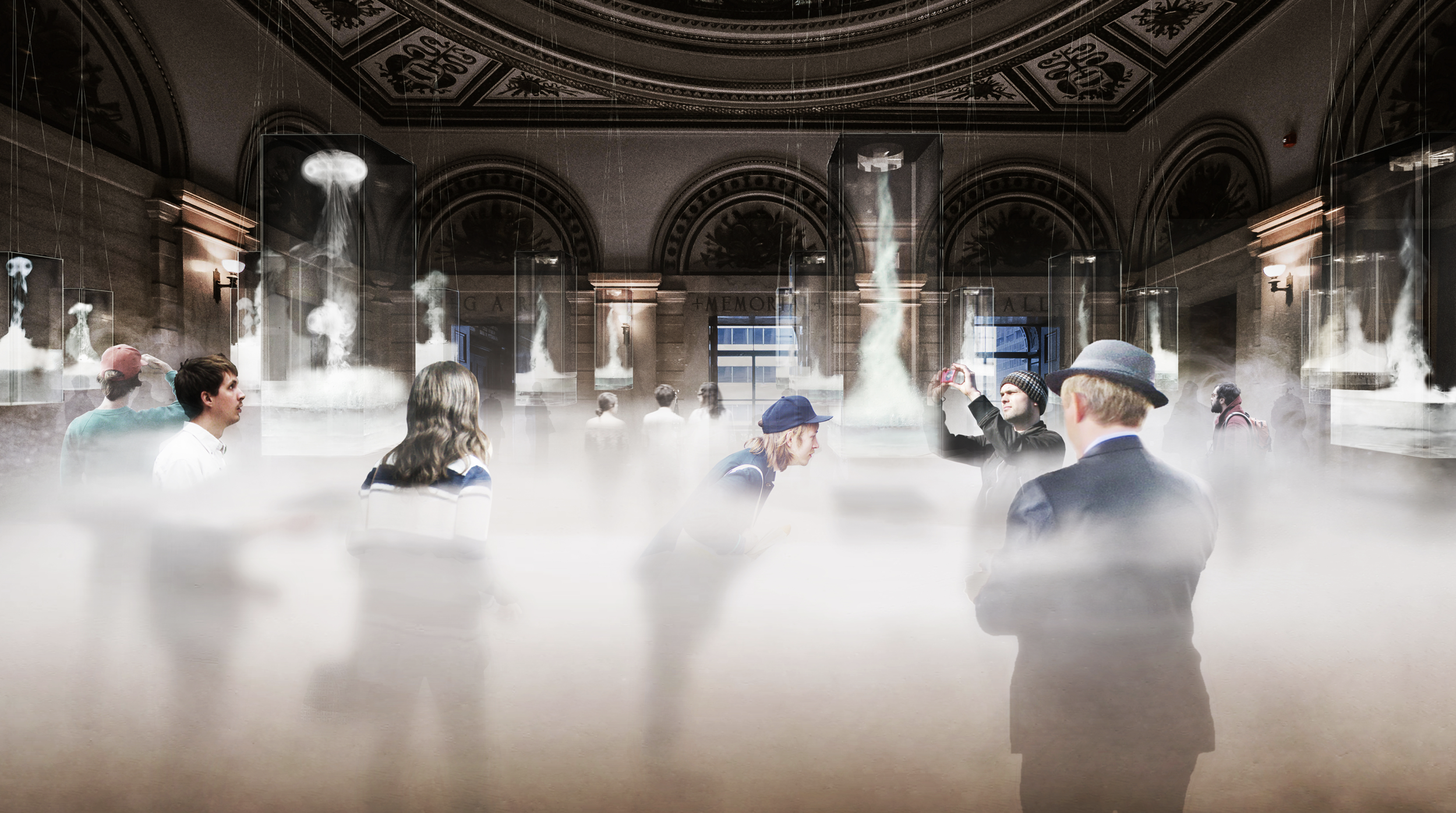
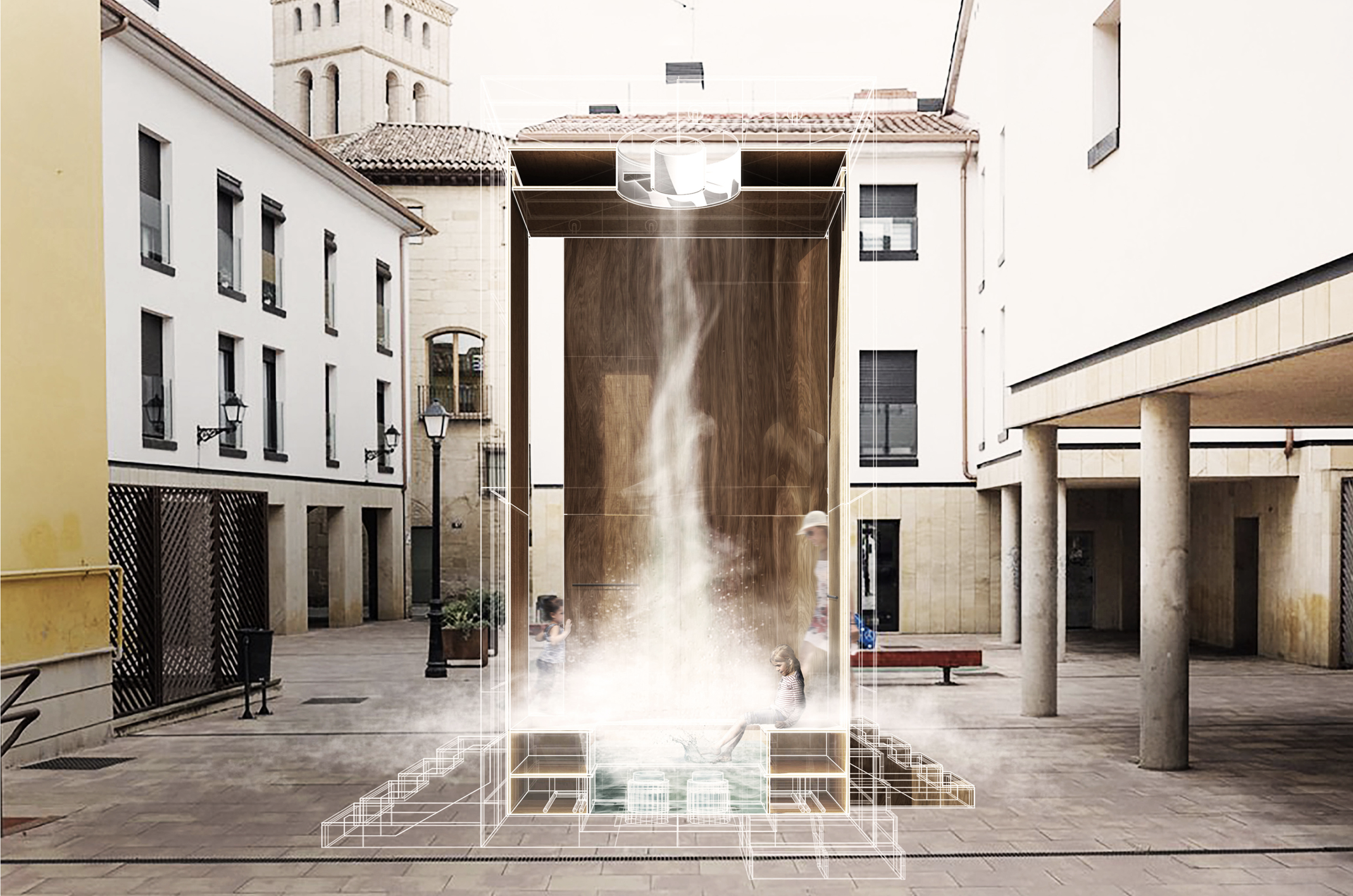
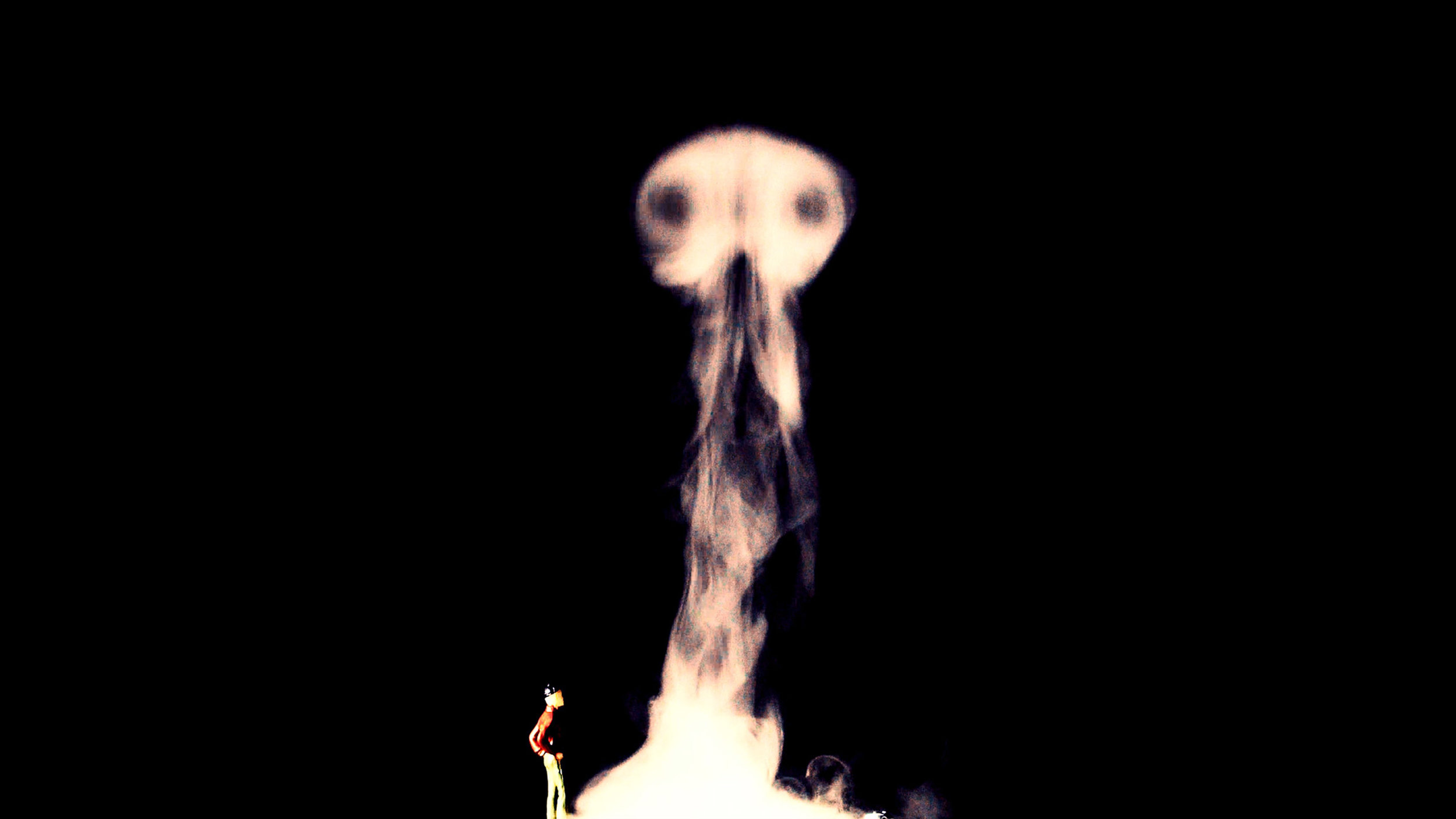
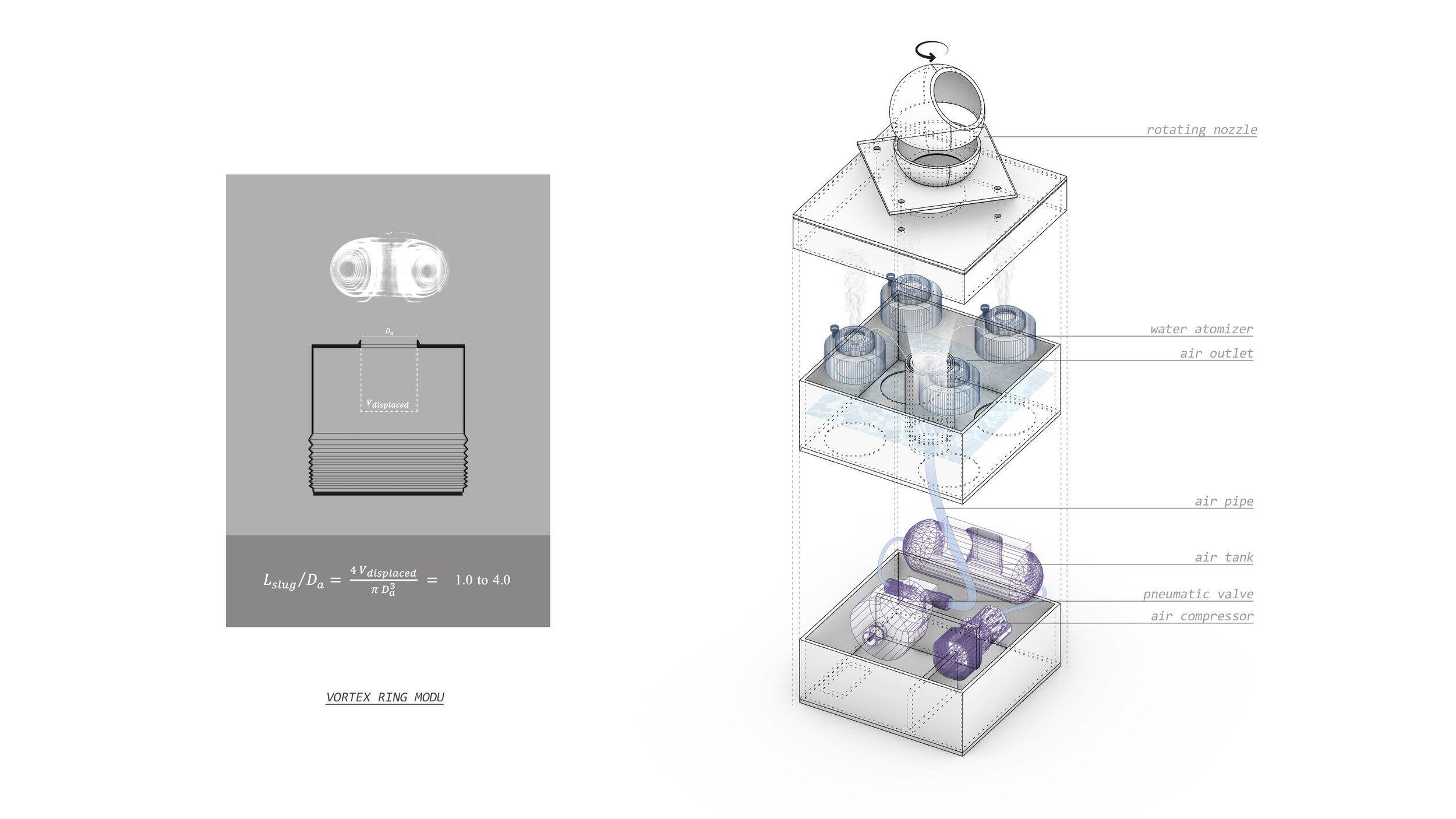
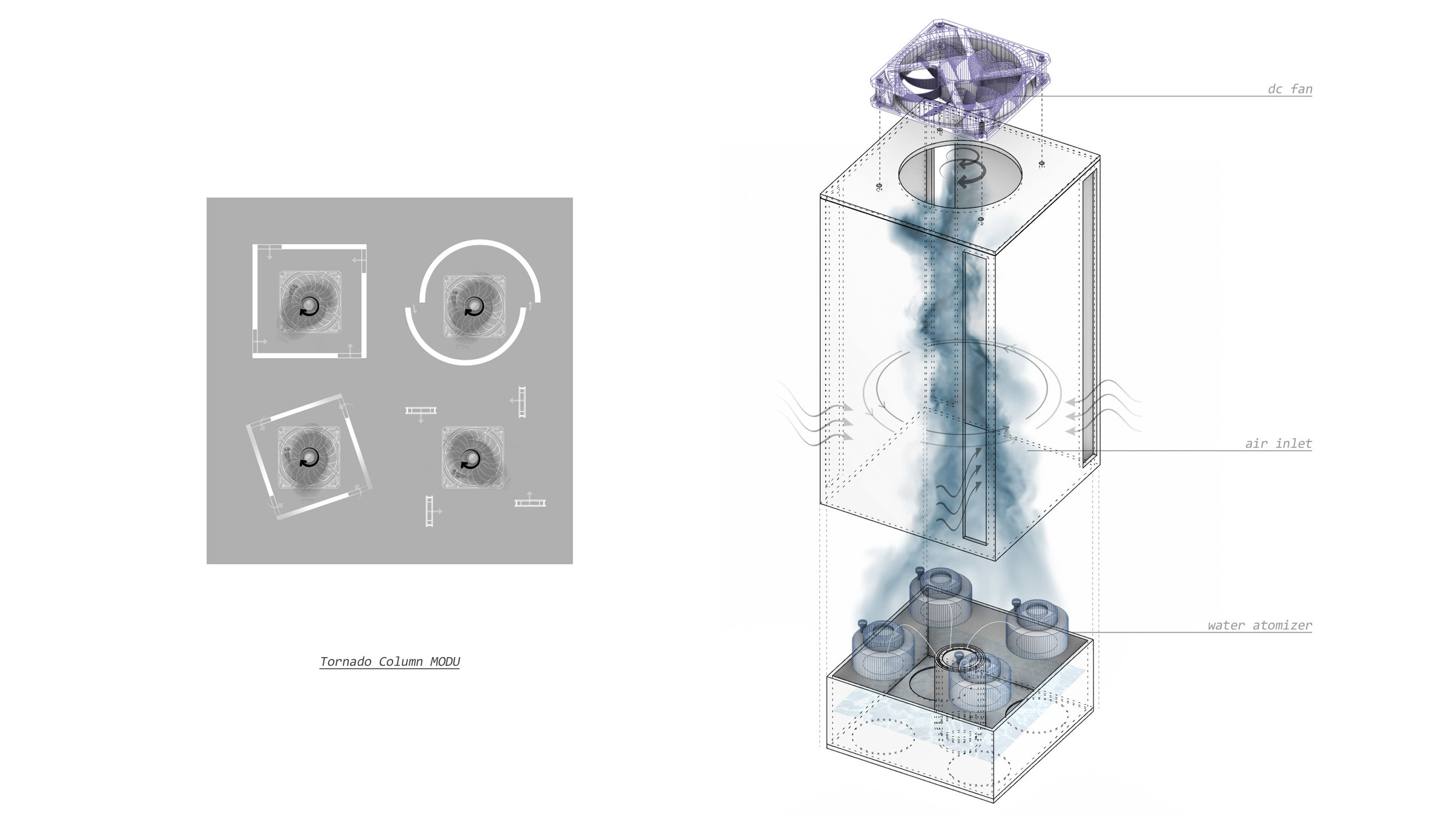
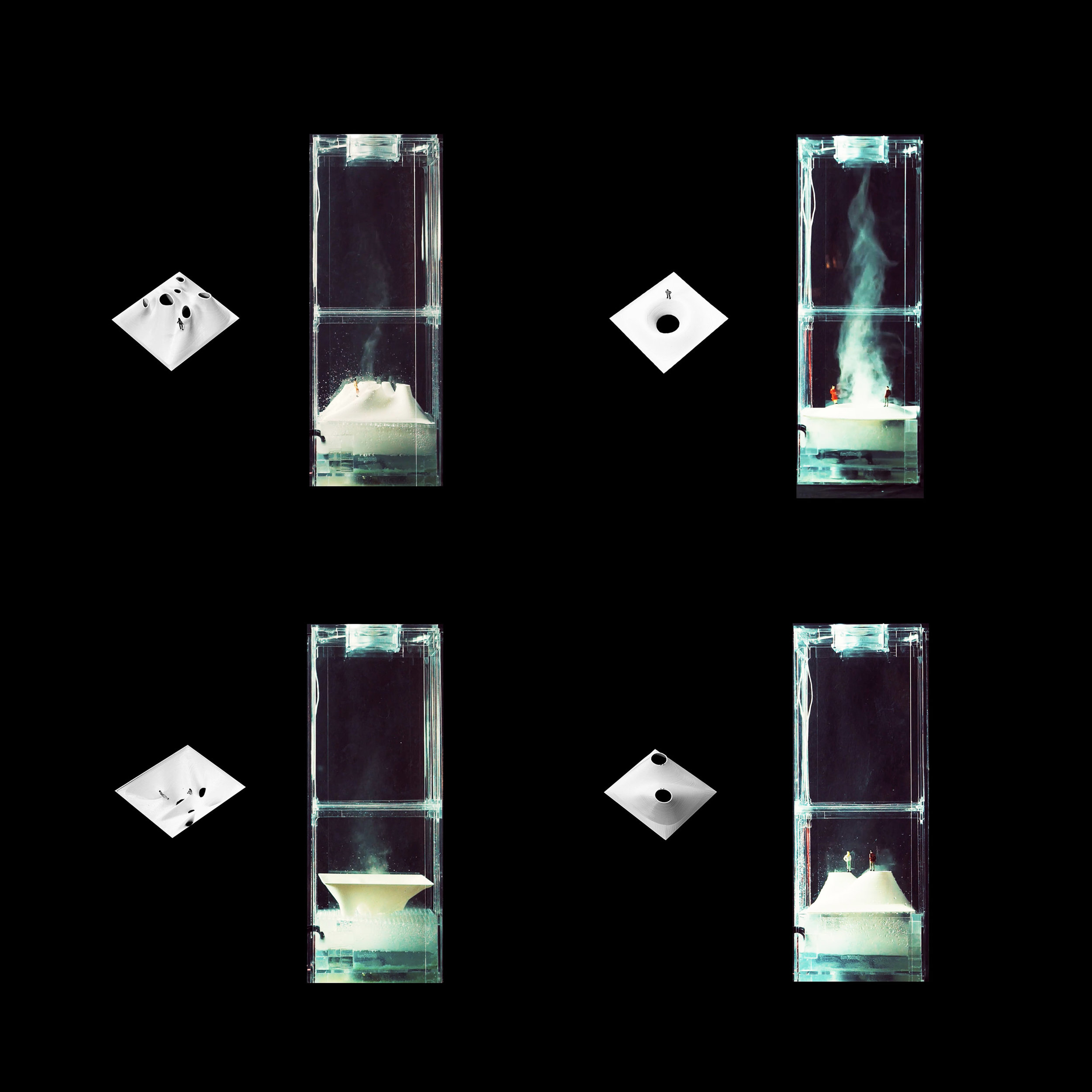
Many of these weather experiences have certain architectural qualities. This project uses vapor as a medium to create the experience of micro-climates and weather conditions from the outside, and bring them back inside architecture as tectonic elements that modulate visibility, create cooling gradients, and produce spatial patterns in a controlled manner. The three main elements are: point – vapor vertex ring, line – vapor tornado, plane – vapor wall. The focused and diffused conditions of vapor enable both localized and global conditions with soft boundaries.
Imagine a future where architects not only sculpt their ideal space but also control the weather inside: one corner feels like the Saharan Desert, while the other behaves like the Amazon rainforest. In one corner, an early morning mist greets the contemplative mind, and in the center space, a focused tornado vapor attracts a gathering crowd. The interior space no longer acts like static and binary units—with clear boundaries like rain for shower, snow for fridge, or sun for light—but like dynamic, diffused, and phenomenal experiences.
Collaborator: Honghao Deng